In intelligent security, health screening, and industrial inspection scenarios, terms like “infrared” and “thermal imaging” are increasingly appearing in our daily conversations. However, many people still have a common misunderstanding: they confuse infrared devices with infrared thermal imagers, and sometimes even think that infrared sensors or temperature guns are the same as thermal imaging equipment.
In fact, this confusion not only affects the correct understanding of the technology’s value but can also lead to wrong decisions during project selection, resulting in ineffective investments.
This article will systematically explain the difference between thermal imaging and infrared, compare various devices, explore their technical advantages, and highlight typical applications. Our goal is to help you clearly distinguish these technologies, understand their unique use cases, and make more rational, precise, and efficient choices.
1. Infrared ≠ Infrared Thermal Imaging: Don’t Confuse the Concepts
1)What is Infrared?
Infrared (IR) is a type of invisible light, part of the electromagnetic spectrum located between visible light and microwaves, with wavelengths roughly between 0.75 micrometers and 1000 micrometers. Although invisible to the human eye, infrared radiation is everywhere — any object with a temperature above absolute zero (-273.15°C) continuously emits infrared radiation.
2)What is Infrared Thermal Imaging?
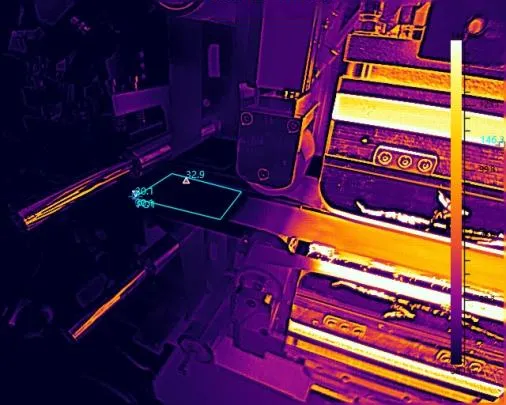
Infrared thermal imaging is a technology that captures the infrared energy naturally emitted by objects and converts the temperature data into visible images. In other words, it transforms “invisible heat” into “visible pictures,” enabling us to detect temperature anomalies and locate heat sources. This technology is widely used in power line inspection, night security surveillance, firefighting and rescue, health screening, and many other fields.
Despite both terms containing “infrared,” infrared refers to a natural physical phenomenon, whereas infrared thermal imaging is a technology developed based on this phenomenon. Therefore, thermal imaging is not the same as infrared, and these concepts should not be confused or used interchangeably.
2.Infrared Devices ≠ Thermal Imaging Devices: Don’t Choose the Wrong Equipment
Although infrared thermal imagers are sometimes called “infrared devices,” they are fundamentally different from traditional infrared equipment we commonly use, such as infrared sensors, temperature guns, and infrared beam detectors.
| Device Type | Working Principle | Imaging Capability | Temperature Measurement | Application Examples |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PIR Sensor (Passive Infrared) | Detects changes in infrared radiation to sense motion | ❌ | ❌ | Automatic doors, lighting control, alarms |
| Infrared Thermometer Gun | Measures infrared from a single point | ❌ | ✅ (Point-based) | Industrial inspection, fever screening |
| Infrared Beam / Laser Sensor | Triggers when beam is interrupted | ❌ | ❌ | Perimeter protection, intrusion alerts |
| Infrared Illuminated Camera | IR light + visible light camera | ✅ (No temp data) | ❌ | Night vision surveillance |
| Thermal Imager (Infrared Camera) | Captures infrared radiation to create thermal maps | ✅ (Thermal imaging) | ✅ (Real-time, wide-area) | Power checks, fire rescue, medical diagnostics |
3. Why Are More and More People Choosing to Invest in Infrared Thermal Imagers?
Infrared thermal imagers capture the infrared radiation emitted by object surfaces to achieve long-distance, non-contact, real-time visual temperature monitoring. They offer the following technical advantages:
- Real-Time Visualization of Temperature Distribution, Quickly Detecting Anomalies
Unlike infrared thermometers that measure temperature at a single point, thermal imaging provides a complete temperature map of the entire scene. This allows for rapid identification of hot spots, cold spots, and abnormal areas, greatly improving inspection efficiency. - Long-Distance, Non-Contact, and High Safety
Infrared thermal imaging can monitor temperatures from a distance without physical contact. It is especially suitable for hazardous environments with high temperatures, high voltage, live electrical equipment, or toxic substances, effectively ensuring personnel safety. - All-Weather Operation, Independent of Visible Light
Thermal imagers do not rely on ambient light, making them effective for stable imaging in darkness, smoke, fog, rain, or snow—conditions where traditional visible-light cameras struggle. - Versatile Use Across Multiple Industries
A single infrared thermal imager can be used for electrical equipment inspection, factory machinery maintenance, building energy analysis, warehouse fire warning, and more. Investing in one device can solve multiple problems. - Smart Integration, Easy Upgrading of Existing Systems
Most online infrared thermal imagers support video streaming, data analysis, and alarm linkage, allowing easy integration into existing security, industrial, or IoT systems for intelligent upgrades. - Cost Continues to Decrease, Lowering Investment Barriers
Thanks to the maturity of uncooled infrared detector technology, the price of infrared thermal imagers has become affordable. Small and medium enterprises, as well as individual users, can now deploy efficient thermal imaging capabilities within reasonable budgets.
4.What Are the Applications of Infrared Thermal Imagers in Civilian Fields?
In the past, infrared thermal imaging equipment was primarily used in advanced fields such as aerospace remote sensing, scientific research, and long-distance target tracking. However, with continuous technological advancements and decreasing costs, infrared thermal imagers have gradually entered frontline industrial applications, security monitoring, health screening, and other civilian markets.
1)Building Energy Efficiency and Hidden Hazard Detection
Issues such as damaged insulation layers, HVAC malfunctions, and poorly sealed doors and windows in building structures often cause significant indoor heat loss that is difficult to detect with the naked eye. Infrared thermal imaging technology can accurately identify thermal bridges, air leaks, and other weak points in energy efficiency.
By visually displaying the temperature distribution on building surfaces in a non-contact manner, thermal imaging not only improves the efficiency of energy-saving renovations but also effectively detects structural hazards such as water leakage, pipe blockages, and wall delamination. This technology is widely used in real estate inspections, home renovations, and green building assessments.
2)Electrical Equipment Safety Inspection
Poor cable connections and abnormal electrical loads often cause abnormal temperature changes. Infrared thermal imaging can quickly identify hotspots at connections, overloaded wires, and aging switchgear without physical contact or power shutdown. Compared to traditional point inspections, infrared detection offers significant advantages such as long-distance, non-contact, and real-time visual monitoring. This improves inspection efficiency and safety while helping to prevent fire hazards and power outages caused by electrical faults.
3)Firefighting and Emergency Rescue
Fire scenes are often accompanied by high temperatures and dense smoke, which severely hinder personnel search and fire source localization. Infrared thermal imagers can penetrate thick smoke and darkness to accurately identify high-temperature zones and locate trapped individuals. This technology is widely used in urban firefighting, forest fire prevention, and emergency response by rescue teams.
Infrared images provide real-time feedback on heat distribution at the scene, helping firefighters make informed decisions and respond quickly. This significantly improves rescue efficiency and operational safety.
4)Perimeter Security Protection
In critical areas such as factory premises, airports, railway lines, and border zones, traditional video surveillance often faces challenges like no light at night, fog, rain, and vegetation obstruction. These factors can make target identification difficult and delay alarms.
Infrared thermal imaging technology captures the heat radiation emitted by intruders—whether humans or vehicles—enabling continuous, long-distance, non-contact monitoring day and night. Even in darkness or complex terrain, thermal imaging provides clear visuals and accurately identifies abnormal heat sources.
When combined with intelligent analysis systems, infrared perimeter monitoring can automatically detect intrusion behaviors and trigger linked alarms. This significantly reduces false alarms and enhances overall security efficiency, making it a crucial technology for building smart, proactive perimeter defense systems.

5)Medical and Health Monitoring
In the medical and health monitoring field, many diseases in their early stages are accompanied by abnormal surface temperature changes, such as inflammation, blood circulation disorders, and localized tissue damage. Traditional thermometers or visual inspection methods often fail to provide a comprehensive view of the body’s condition.
Infrared thermal imaging technology enables non-contact, real-time acquisition of the human body’s surface temperature distribution, allowing intuitive detection of abnormal temperature zones. This effectively assists doctors in preliminary screening and clinical diagnosis.
Especially in large-scale temperature screenings, chronic disease rehabilitation, and sports injury assessment, infrared thermal imagers offer advantages such as radiation-free operation, rapid response, and no physical contact. These benefits not only improve detection efficiency but also reduce the risk of cross-infection.
5. Recommended Infrared Thermal Imaging Devices
To meet the diverse needs of users, the following are two representative product recommendations from the Raythink brand
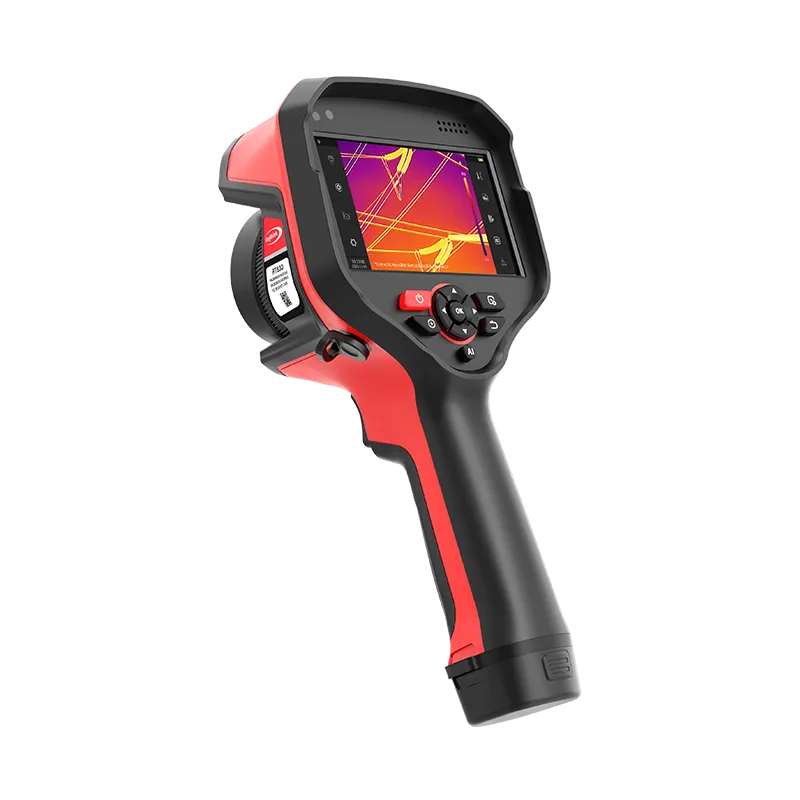
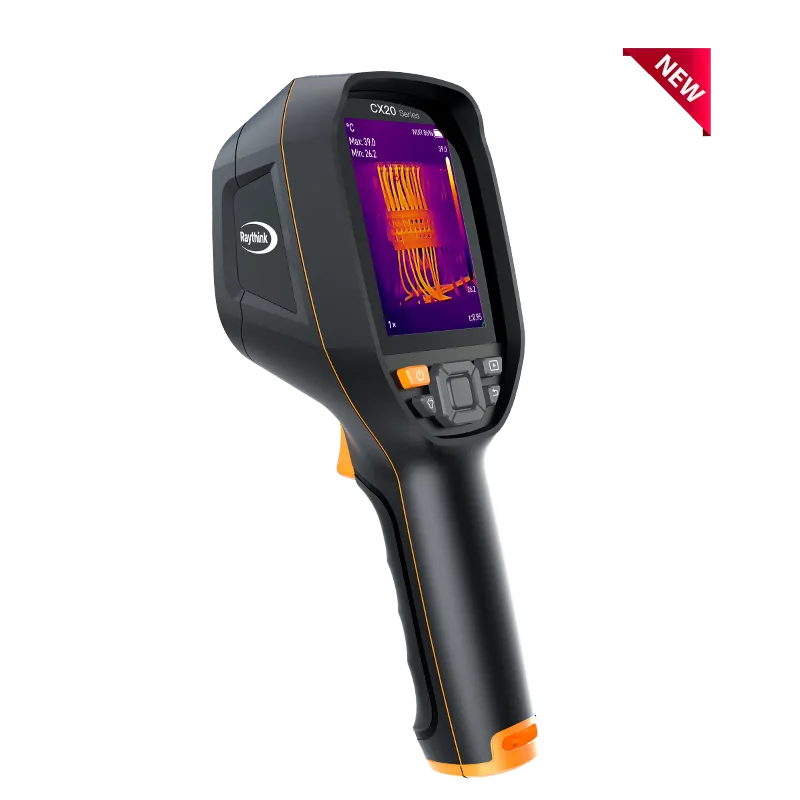
1)Portable Handheld Thermal Imagers
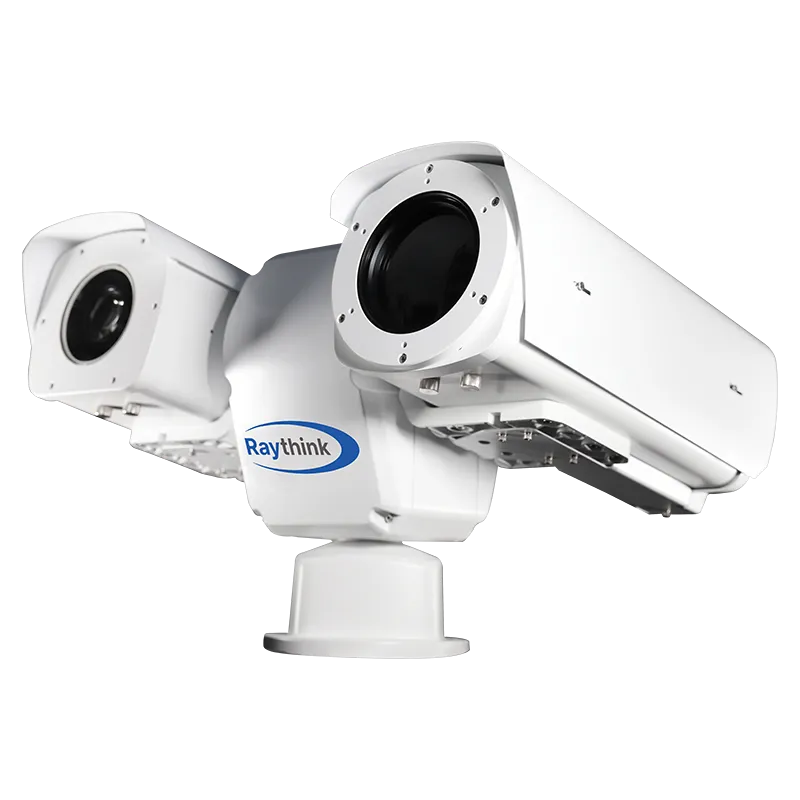
2)Fixed-Mount Thermal Imagers
Raythink Technology offers a comprehensive product portfolio tailored to various application scenarios. Different environments require specific parameters such as resolution, temperature measurement range, and lens field of view. To ensure more accurate product selection and efficient deployment, we recommend contacting the Raythink technical consultant team for expert advice once your usage requirements are defined.
Conclusion: Understanding Infrared Fundamentals is Key to Making the Most of Infrared Thermal Imaging
Infrared thermal imaging transforms invisible temperature differences into visible images, enabling faster problem detection and response. It has become an essential technology in intelligent security, industrial inspection, health monitoring, and many other fields.
Raythink Technology is deeply committed to advancing infrared thermal imaging, focusing on providing accurate and reliable infrared sensing solutions tailored to various industries. For expert advice on product selection, application consultation, or technical support, please feel free to contact the Raythink technical team.