In today’s era of rapid digitalization and urbanization, the demand for security is steadily increasing. From urban public safety and critical infrastructure protection to the daily security of corporate campuses and residential communities, surveillance technology has become an indispensable part of modern society.
Currently, most security systems still rely on traditional CCTV (visible-light cameras). These devices provide clear images in daylight or well-lit environments, but at night, in dark areas, or under adverse weather and complex conditions, they often suffer from blind spots and limited recognition capabilities. For example:
- Nighttime monitoring depends heavily on supplementary lighting; without it, the footage is completely dark.
- Rain, snow, and haze can cause significant image degradation.
- Supplementary lighting exposes the camera’s position, reducing concealment.
- CCTV can only capture surface appearances and cannot detect hidden risks such as abnormal heat that may signal fire hazards or equipment failures.
Due to these limitations, CCTV is more suitable for well-lit, routine environments but falls short of independently handling 24/7 security tasks in complex or high-risk scenarios.
With advancements in infrared imaging and artificial intelligence, thermal security cameras are becoming a critical component of modern security systems. By detecting infrared radiation emitted by objects, they deliver truly all-weather monitoring with minimal reliance on lighting conditions, while also enabling the early detection of potential threats. This provides a new, more reliable solution for comprehensive security in the digital age.
1.Working Principle of Thermal Security Cameras
1) Fundamentals of Infrared Radiation
Any object with a temperature above absolute zero (–273.15°C) emits infrared radiation in the form of electromagnetic waves. The intensity and wavelength distribution of this radiation are closely related to the object’s temperature. Although the human eye cannot perceive infrared radiation directly, a thermal security camera uses highly sensitive detectors to capture this invisible energy and convert it into digital signals.

2) Imaging Mechanism
The imaging process of a thermal security camera generally includes the following steps:
- Infrared Detection:The detector receives infrared radiation emitted by the target object.
- Signal Conversion:The infrared radiation converted into electrical signals and then amplified for processing.
- Image Generation:Image processing algorithms map different radiation intensities to varying levels of grayscale or pseudo-colors, thereby creating a visualized thermal image.

In thermal images, high-temperature areas are typically displayed in bright or warm colors, while low-temperature areas appear in dark or cool tones. These colors do not represent actual visible-light hues; rather, they are a visual enhancement designed to emphasize temperature differences. This makes it possible to intuitively detect abnormalities in people, animals, or equipment, even in complex or challenging environments.
3)Technology Trends
With the widespread adoption of uncooled infrared detectors, such as vanadium oxide microbolometers, thermal security cameras have become more compact, sensitive, and cost-effective. Today’s high-end devices can achieve thermal resolutions of 0.04–0.05 °C under standard testing conditions—typically around 25 °C ambient temperature, with minimal temperature difference between the target and background, and NETD below 40–50 mK. This capability allows them to detect extremely subtle temperature variations, providing a solid technical foundation for early warning in security applications.

2.Key Advantages: Thermal Imaging vs. Traditional CCTV
1)All-Weather Monitoring vs. Light Dependency
Traditional CCTV relies on visible light to capture images. While it can deliver high-resolution footage during the day or in well-lit conditions, nighttime or low-light environments require supplementary or infrared lighting. Even with these aids, monitoring coverage and image clarity remain severely limited: the effective range of supplementary lights is restricted, resulting in blurred edges or blind spots. Additionally, heavy reliance on auxiliary lighting increases energy consumption and can contribute to light pollution. More importantly, the lights themselves reveal the camera’s location, compromising the concealment of the security system.
Thermal security cameras operate on a completely different principle. By detecting the infrared radiation emitted by objects, they do not depend on external light sources at all. Whether it’s day or night, sunny or overcast, rainy, foggy, smoky, or even in complete darkness, thermal cameras provide stable, clear, and reliable monitoring footage under all conditions.
In the Same Nighttime Scene
Application Case:
During nighttime highway surveillance, conventional cameras often struggle to detect pedestrians or obstacles in unlit areas, limiting their effectiveness in traffic incident warnings. In contrast, thermal security cameras can directly capture the heat signatures of humans or vehicles. Even at long distances and in complete darkness, they provide clear identification, enabling timely alerts and significantly enhancing road safety.
2)Detecting Potential Threats in Advance vs. Post-Incident Evidence
The core function of CCTV is to provide video records, with its primary value lying in post-incident evidence collection. Relying solely on CCTV for security management often means that threats are only documented after damage has occurred. This reactive approach cannot meet the demand for proactive prevention in high-risk scenarios.
Thermal security cameras, on the other hand, offer a unique early-warning capability. They can detect temperature anomalies invisible to the naked eye, providing alerts before risks fully materialize. Examples include:
- Intruder detection:Even when intruders are concealed in darkness, their body heat is significantly higher than the surrounding environment, making them clearly visible.
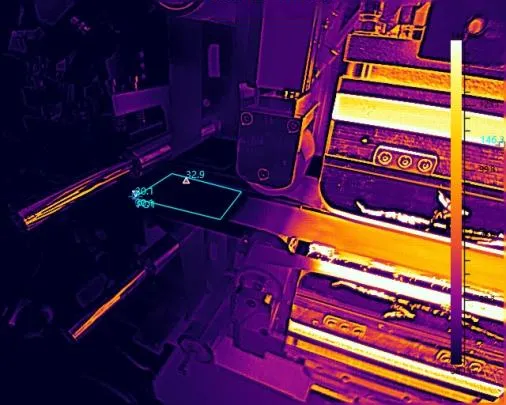
- Equipment hazards:Electrical equipment, pipeline valves, or storage tanks often exhibit Bbnormal heat generation during early-stage malfunctions. Thermal imaging allows these risks to be identified and addressed before accidents occur.
This capability shifts security systems from a passive, post-incident evidence model to an active, preventive approach, enabling risk management ahead of time. Such a distinction is particularly critical for highly sensitive areas like petrochemical plants, substations, or airports.
Of the Same Fire Spot Scenario
3)Intelligent Compatibility vs. High False Alarm Rate
In low-light or nighttime conditions, traditional CCTV often misidentifies objects due to blurred images. For example, moving shadows, light reflections, or small animals can be mistakenly recognized as intrusions, leading to frequent false alarms. This not only wastes manpower but also causes alarm fatigue among security personnel, reducing the effectiveness of emergency response.
Thermal security cameras leverage temperature-based target recognition, significantly improving detection accuracy. When combined with modern intelligent video analytics systems, thermal imaging can determine whether a target is human and even analyze its behavior. For instance, it can distinguish animal activity from unauthorized entry or detect loitering and climbing actions. By integrating temperature characteristics with behavioral analysis, false alarm rates are greatly reduced, enhancing the reliability and credibility of system alerts.
Typical Application: In oilfield perimeter security, conventional CCTV often struggles to differentiate small animals from actual intruders at night, resulting in frequent false alarms. Thermal cameras, combined with AI-based behavior analysis, can accurately identify human targets, ensuring security resources are efficiently allocated.
4)Environmental Adaptability vs. Imaging Limitations
The imaging performance of CCTV heavily depends on visible light conditions. In environments such as haze, dust storms, heavy rain, or strong backlighting, image quality can degrade significantly, sometimes rendering monitoring completely ineffective. For security systems that need to operate outdoors or in complex settings over extended periods, this represents a critical limitation.
Thermal security cameras, based on infrared radiation imaging, do not rely on visible light and are therefore insensitive to external lighting conditions. Whether during day or night, under strong backlight, or in dense fog and smoke, they maintain stable operation. Even in extreme environments, thermal imaging can clearly distinguish targets from the background based on temperature differences, ensuring continuous and reliable security monitoring.
In the Same Nighttime Scene
Typical Application: In ports, airports, or forest fire monitoring, traditional CCTV often produces blurred images due to weather conditions, limiting its effectiveness. In contrast, thermal security cameras maintain clear monitoring under the same conditions, enabling security personnel to detect anomalies immediately and reduce potential safety risks.
3. Recommended Raythink Thermal Security Camera Solutions
4. Typical Application
1)Perimeter Protection
In critical areas such as airports, ports, defense facilities, research centers, and large warehouse complexes, perimeter protection forms the first line of defense in a security system. If the perimeter is breached, intruders may gain direct access to core facilities, posing serious security risks.
Thermal security cameras detect the heat signatures of humans, enabling accurate identification of intrusions even at night, in fog, rain, or low-light conditions. The system can display intrusion locations in real time and trigger perimeter alarms for immediate response. Moreover, thermal imaging can cover vast areas without the need for supplementary lighting, reducing blind spots and alleviating the burden on security patrols.
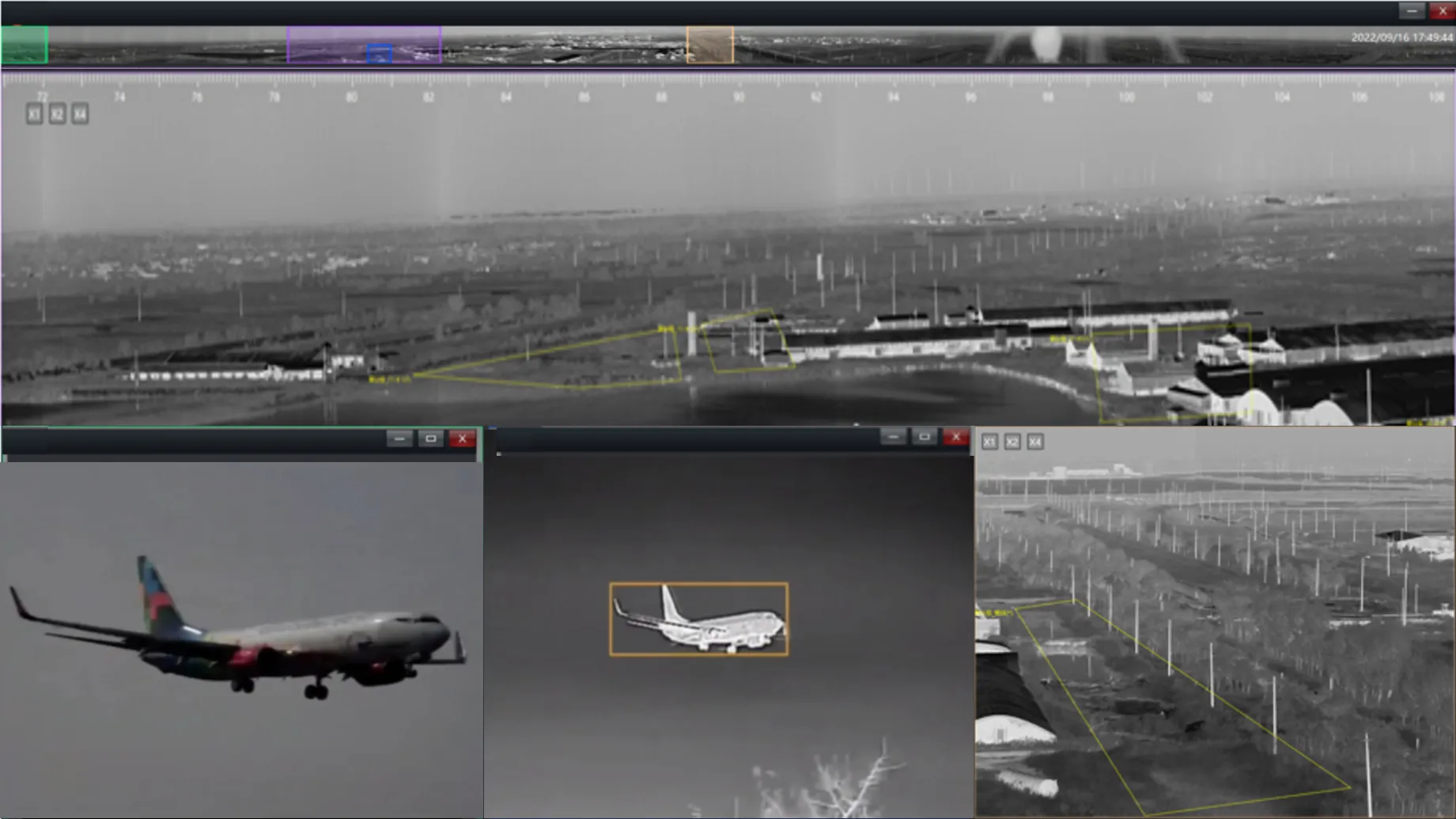
2)Nighttime Monitoring of Tunnels and Highways
Transportation is a core component of urban and regional operations, and highways and tunnels often operate in low-light or completely dark conditions. Vehicle breakdowns, illegal parking, or pedestrians entering restricted areas can all lead to serious accidents.
Thermal security cameras can detect the heat signatures of vehicles and pedestrians even in total darkness, while also identifying potential fire hazards and abnormal heat sources. With real-time thermal imaging and intelligent analytics, authorities can promptly spot risks, take immediate action, and ensure traffic safety as well as efficient emergency response.

3)Oil Depots, Power Plants, and Substations
Security breaches or fires at energy facilities can result in severe economic and social consequences. Thermal security cameras not only help prevent unauthorized access but also provide real-time monitoring of equipment temperatures, detecting abnormal heat sources caused by electrical overheating or oil and gas leaks. This dual-function monitoring ensures the safe and reliable operation of critical energy infrastructure.

4)Nighttime Crowd Management and Fire Hazard Detection
During large-scale events or emergency operations, nighttime crowd monitoring is a critical task. Thermal security cameras can accurately identify crowd distribution and gathering trends, providing reliable data even in low-light conditions. At the same time, they can detect abnormal heat signatures within the field of view, assisting in the early identification and prevention of potential fire hazards.

5. Usage Recommendations
1)Proper Installation Height and Angle
Choosing the appropriate installation height and tilt angle based on the characteristics of the monitored area is critical. Installing cameras too high may result in loss of detail, while too low may cause obstructions. It is generally recommended to position cameras within a 3–6 meter range and adjust the angle according to the specific scene to achieve optimal coverage.
2)Integration with Intelligent Alarm Systems
The true value of thermal security cameras lies in their integration with intelligent systems. By defining alert zones, behavior rules, and anomaly thresholds, the system can automatically link with intelligent alarm systems and trigger smart alarms when potential threats are detected, reducing reliance on manual patrols.
3)Regular Calibration and Lens Maintenance
Thermal imaging devices require regular calibration of the detectors to ensure accurate temperature difference detection. The lenses should also be kept clean to prevent dust, moisture, or oil from affecting image quality. For equipment used outdoors over long periods, it is recommended to add sunshields or protective housings.
6.Conclusion
In modern security systems, traditional CCTV still holds value, but its application is limited by lighting conditions and imaging environments, making it more suitable for low-risk, well-lit, routine scenarios. In contrast, thermal security cameras demonstrate irreplaceable advantages in high-risk, complex, and all-weather security situations.
They not only overcome the inherent limitations of conventional CCTV but also enable a shift from “post-event evidence” to “preemptive prevention” through intelligent analysis. Whether for perimeter protection, traffic safety, energy facilities, or crowd management, thermal cameras are driving security systems toward greater efficiency, intelligence, and proactive monitoring.
Looking ahead, with the further integration of artificial intelligence and big data technologies, thermal security systems will continue to advance in automated monitoring, behavior recognition, and risk prediction, becoming a cornerstone of smart cities and intelligent security.
Raythink thermal security cameras, with their outstanding performance and intelligent compatibility, will continue to provide users with customized solutions, comprehensively enhancing all-weather security capabilities and establishing a solid shield for safety and stability.










